
Implementing a Break-Even Plan in Small Business
In the challenging world of small business, acquiring a fine balance between revenue and expenses is pivotal. Often, the ambition of many small business owners is not just to survive but to thrive. It is here that understanding and reaching the break-even point becomes crucial. Implementing a break-even plan is indispensable in stabilizing your business and setting the stage for robust financial health. Let’s delve into the profound mechanics of creating a break-even plan that works.
Understanding Break-Even
To start with, let’s demystify what break-even truly means. It is the point where your total revenue equals your total expenses. Beyond this point, every additional pound or dollar of revenue translates to net profit. Understanding your break-even point assists in setting realistic goals, pricing strategies, and cost control, allowing maximum utilization of resources and driving sales effectively.
The break-even plan is a multifaceted plan to cut expenses just enough to stop the bleeding of cash while relentlessly selling enough to cover your essential costs including personal drawings and debt service.
So, we want to minimise expenses while driving sales so we can get the business up into that net profit zone and that’s what’s going to allow us to have positive cash flow which we use to cover personal drawings and service debt obligations.
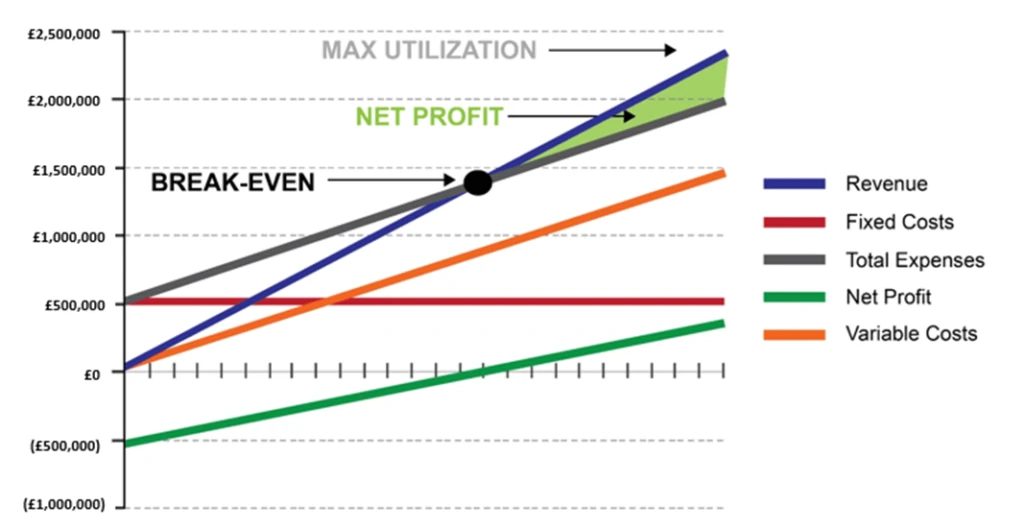
Let’s take a look on this chart. It’s really important for a business owner to understand this break-even graph and how it works particularly the concepts of break-even, net profit and maximum utilization.
The dark red line represents your fixed costs, including your overhead and administrative salaries.
The orange line represents variable costs which is made up of basically labour and the materials required to make the goods being produced, or it may just be the labour required to deliver services.
When you add fixed and variable costs together you the total expenses represented by the grey line. The goal of the business is to generate enough revenue represented by the blue line to exceed the total expenses.
The point at which the revenue line crosses the total expense line which is where revenue equals total expenses is called the break-even point. Just below the £1.5m in this instance.
In order for the business to break even it has to start by covering its fixed costs. Every business has a certain amount of fixed costs that are essential to running the business and the goal is to get this fixed cost as low as possible. Fixed costs are items like premises rent, insurance expenses or equipment leases.
The thing about fixed costs compared to variable costs are that fixed costs have almost no connection whatsoever to sales volume. So, if the business goes through something traumatic or is affected by an economic downturn or something like that the fixed costs don’t go away, and that’s a big downside to fixed costs. They don’t typically change or go away without overhauling the business.
So, every business needs to have a certain number of sales to cover their fixed costs and that becomes a challenge for businesses that are running at or below break-even.
Now, all these concepts can be depicted as a mathematical function. The big overall formula is break even = fixed costs ÷ gross profit margin percentage.
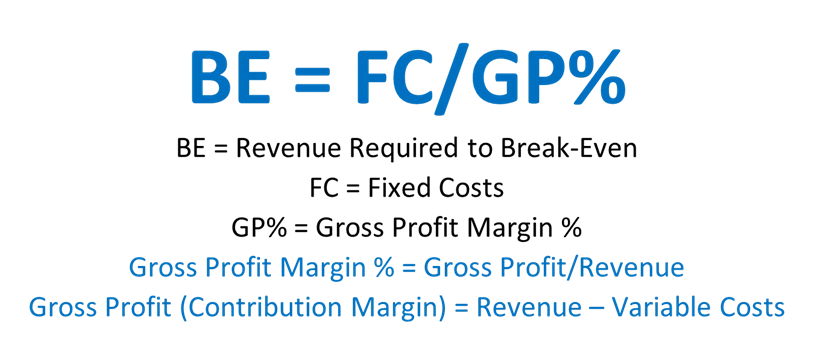
Let’s break that down into two components.
Break-Even (Step 1 – Gross Profit %)
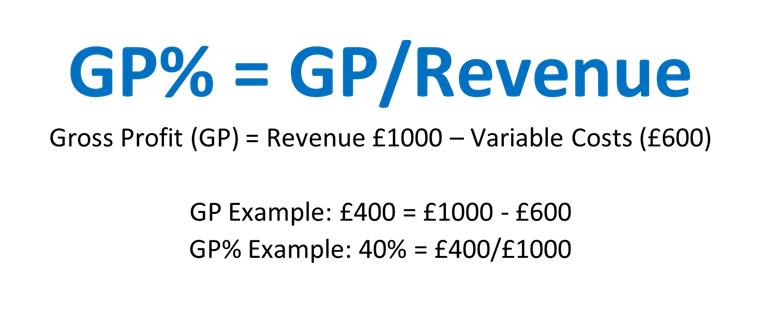
Let’s start with your GP%.
Surprisingly, many business owners don’t understand what their GP% is.
So let me walk you through this example.
Gross Profit = your revenue – your variable costs.
And your gross profit percentage is just your gross profit divided by your revenue.
So, in our example, our gross profit is 400 and our revenue is 1000 so our gross profit % is 40%.
Now that we know our gross profit percentage, we can determine our break-even point.
Break-Even (Step 2)
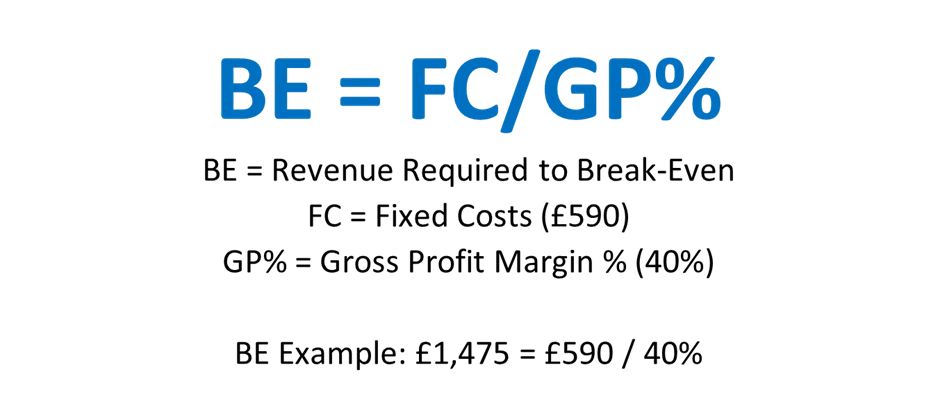
Our breakeven point is when our gross profit will cover our fixed costs.
So, you can see in the example below if our fixed costs are £590 and our gross profit margin is 40%
Our break-even is £1,475.
So back to our graph that we saw earlier – we can see that in 000’s our breakeven point is £1.475m.
This is important to know – as the famous saying goes – if you can’t measure it you can’t manage it.
So, understanding your breakeven point and being able to evaluate your fixed costs to bring that Break-Even point down.
To implement a Break-Even Plan what we do is:
1. Start with Fixed and Variable Costs
Carefully identify these expenses; discerning between the fixed and variable costs offers a clear view of your operating costs and lays the foundation for a more sustainable financial strategy.
2. Calculate Total Expenses
After scrutinizing your fixed and variable costs, you need to add them together to compute your total expenses. This sum is crucial; it unveils the revenue needed to cover all operating costs, thus signifying your break-even point.
3. Evaluate Your Revenue Streams
Next, examine your revenue streams meticulously. Revenue is the lifeblood of your business, and its sources might vary. Evaluate each product or service you offer and determine its contribution to the overall revenue. Assessing each revenue stream individually enables the identification of more profitable areas, aiding in resource allocation and driving sales strategically.
4. Align Prices with Costs
One of the pivotal steps in realizing break-even is aligning your pricing structure with your costs. This alignment ensures that each unit sold contributes adequately to covering your fixed costs and generating a net profit. Properly structured pricing is instrumental in maintaining a healthy profit margin and achieving financial stability.
5. Optimize Operations for Maximum Utilization
Focus on refining your operational strategies for maximum utilization of resources. Streamlined operations coupled with efficient resource utilization drive down costs and accelerate the journey to the break-even point. Regularly review your operational processes and adapt them to minimize waste and enhance productivity.
6. Reduce Non-critical Expenses
In a small business, prudence in managing non-critical expenses is invaluable. Such expenses, while seemingly insignificant, can accumulate and impair your financial stability. Scrutinize your expense list and distinguish between essential and non-essential costs. Consider minimizing or eliminating non-critical expenses until you achieve a healthy financial state.
7. Address Debt Service and Personal Drawings
Debt service and personal drawings can substantially impact your break-even point. Regularly review your debt service commitments and structure them efficiently to mitigate their impact on your cash flow. Similarly, exercise restraint with personal drawings to retain more profits within the business, hastening the attainment of your break-even point.
8. Prioritise Driving Sales
Driving sales is fundamental to increasing revenue and reaching your break-even point sooner. Develop comprehensive sales strategies focusing on high-margin products or services. Elevate your marketing efforts and enhance your sales team’s skills to optimize sales performance.
9. Monitor and Adjust Regularly
A break-even plan is not a set-it-and-forget-it tool. Regular monitoring and adjustments are paramount. Market conditions, customer preferences, and costs are dynamic; hence, adapt your break-even plan accordingly. Analyse your financial statements periodically and adjust your strategies to maintain alignment with your break-even goals.
10. Incorporate Technology
In today’s digital age, integrating technology can revolutionize your break-even plan. Utilise software and tools to track and analyse your costs, revenue, and other financial metrics effectively. Technology can provide real-time insights, allowing swift and informed decisions, which are crucial for maintaining financial equilibrium.
Conclusion
Implementing a break-even plan is a meticulous yet rewarding process. It starts with understanding your fixed and variable costs, calculating your total expenses, and analysing your revenue streams. Aligning your prices with costs and optimizing operations for maximum utilization are key steps towards achieving financial balance. The reduction of non-critical expenses, structured management of debt service, and personal drawings, and a relentless focus on driving sales are integral components of a well-rounded break-even plan.
I recently held a 30-minute webinar for business owners who are struggling to turn around a business in financial difficulty.
In this webinar, I show you exactly what I learned as a CEO turning around several businesses facing financial difficulty and as a business coach helping business owners across the world turn around their own businesses. You can watch the replay here.
IMPORTANT: if you’re in sound financial shape and ready to take your business to the next level, there is no need to wait for the webinar. You can explore if a Business Coach would be a fit by booking an initial complimentary 15-minute call with me at TimeWithShane.com.


